A database is a collection of structured data that can be accessed with specific commands. WordPress uses the open-source MySQL relational database to store your posts, pages, usernames and other important information. The fact that MySQL (and other database formats) are relational means that various pieces of data can be related. For example, a post is “related” to various images attached to it.
In order to use WordPress, you only need to understand a few things about its database.
1) WordPress recommends MySQL version 5.6, but can run on MySQL 5.0.
2) You should have an automatic backup plan that backs your database up.
3) You need to create a MySQL database and a database user (and password) in order to install WordPress.
4) Your database name, database username, and the username’s password go into your wp-config.php file.
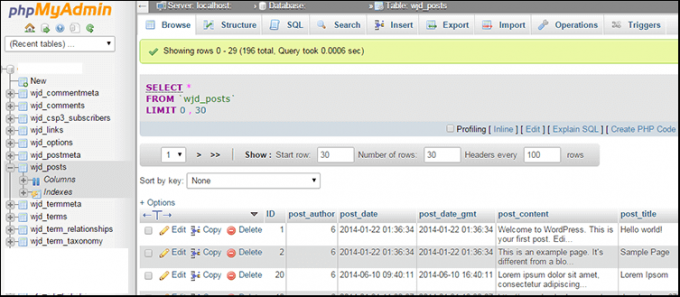
If you want to learn more about your WordPress database, you use a Cpanel tool called phpMyAdmin. With this tool, you’ll be able to browse your WordPress database, and even change its contents. Of course, modifying the database contents directly is for experts only!
Here’s what a WordPress database looks like, when viewed with phpMyAdmin. Notice the row and column structure, similar to a spreadsheet.