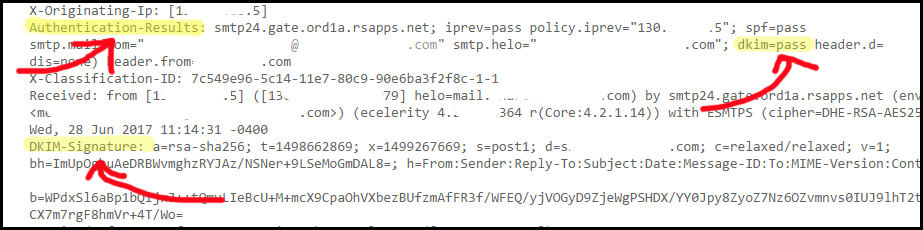
DomainKeys Identified Mail (DKIM) is an email authentication method for minimizing email spoofing. It allows a receiving email host to verify that the sending domain is authorized by the owner of the domain. This is all done by the mail servers themselves, and is transparent to end-users.
Ask your email host (which may or may not be your web host) if they support DKIM. If so, they can help you set it up on your own outbound mail by adding a TXT record that contains your public key to your DNS.
A sample DKIM TXT record will look something like this:
TXT default._domainkey.example.com. “v=DKIM1;p=SLKDJNcjf3gjslkd008GLSKDFjflkjJF39&9374LKDJFYj342AFU43jKDFJ&GHLK3J3”
Once configured, your email headers will include a public DKIM signature, and a header indicating that the message passed DKIM authentication.
The headers will look something like this: